Proteins that manipulate apoptosis of host cells and/or inhibit a multitude of host cytokines. The interferonresponse system is targeted in many ways by poxvirus-encoded factors acting before and after IFN production. Usually this involves binding and neutralization of IFN molecules. Poxviruses also target specific enzymes in IFN-dependent pathways, such as protein kinase R. In this prospective multicenter cohort study of 950 elderly patients with acute symptomatic VTE, we found that adherence to five recommended processes of care was variable and partially suboptimal. The adherence rate varied from 86% for treatment with parenteral anticoagulants for at least five days to a mere 35% for continued treatment with LMWH in patients with active cancer. Overall, our findings are consistent with prior studies demonstrating that the use of recommended processes of care and the achievement of treatment goals for patients with VTE leaves room for improvement. If anything, adherence rates were even lower in our elderly populationfor Eleutheroside-E several processes of care than in previous studies enrolling younger patients with VTE. Compared to a retrospective study of U.S. veterans in which oral anticoagulation was initiated on the first treatment day in 64% of cases, we 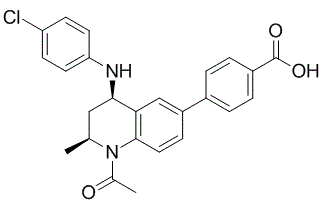 found a substantially lower rate in our study sample. In a prospective study of Canadian outpatients with VTE, 60% of patients with cancer-related VTE received LMWH monotherapy compared to 35% in our study. While the proportion of patients who had parenteral anticoagulation continued until an INR value $2.0 for 24 hours was 37% only in our sample, this target was achieved in about 50% of patients in younger patients. Our results demonstrating a low adherence rate to anticoagulation-related processes of care in elderly patients are consistent with prior evidence showing that the rate of anticoagulation is low in hospitalized elderly patients with atrial fibrillation. Elderly, multimorbid Nafcillin Sodium medical inpatients have also a low rate of venous thromboprophylaxis. It remains unclear whether the low adherence rate is due to lack of physicians’ knowledge, physicians’ fear to induce bleeding, the presence of comorbid conditions that are not compatible with guideline adherence, or patient preferences. For instance, elderly patients with cancer who develop VTE are more likely to have severe renal failure and therefore, may not be candidates for extended LMWH treatment. Similarly, although LMWHs seem to be acceptable to patients with cancer, many elderly patients may prefer to receive oral anticoagulants rather than daily injections with LMWH. One study found that 30% of physicians did not believe it is necessary to have a therapeutic INR for $2 days before discontinuing heparin. Prior evidence about the effect of age on VTE-related anticoagulation practices is limited. While age did not influence the duration of anticoagulant therapy in one study, older patients were more likely to have continuation of parenteral anticoagulation until INR was $2 for 24 hours in another study. In an Italian registry, compression stockings were 1.6 times more likely to be prescribed in patients aged 40�C60 years than in patients aged.80 years. To our knowledge, there are no studies examining the effectiveness of interventions to improve anticoagulation-related processes of care for established VTE. Although evidence from studies on VTE prophylaxis suggests that active, multifaceted strategies.
found a substantially lower rate in our study sample. In a prospective study of Canadian outpatients with VTE, 60% of patients with cancer-related VTE received LMWH monotherapy compared to 35% in our study. While the proportion of patients who had parenteral anticoagulation continued until an INR value $2.0 for 24 hours was 37% only in our sample, this target was achieved in about 50% of patients in younger patients. Our results demonstrating a low adherence rate to anticoagulation-related processes of care in elderly patients are consistent with prior evidence showing that the rate of anticoagulation is low in hospitalized elderly patients with atrial fibrillation. Elderly, multimorbid Nafcillin Sodium medical inpatients have also a low rate of venous thromboprophylaxis. It remains unclear whether the low adherence rate is due to lack of physicians’ knowledge, physicians’ fear to induce bleeding, the presence of comorbid conditions that are not compatible with guideline adherence, or patient preferences. For instance, elderly patients with cancer who develop VTE are more likely to have severe renal failure and therefore, may not be candidates for extended LMWH treatment. Similarly, although LMWHs seem to be acceptable to patients with cancer, many elderly patients may prefer to receive oral anticoagulants rather than daily injections with LMWH. One study found that 30% of physicians did not believe it is necessary to have a therapeutic INR for $2 days before discontinuing heparin. Prior evidence about the effect of age on VTE-related anticoagulation practices is limited. While age did not influence the duration of anticoagulant therapy in one study, older patients were more likely to have continuation of parenteral anticoagulation until INR was $2 for 24 hours in another study. In an Italian registry, compression stockings were 1.6 times more likely to be prescribed in patients aged 40�C60 years than in patients aged.80 years. To our knowledge, there are no studies examining the effectiveness of interventions to improve anticoagulation-related processes of care for established VTE. Although evidence from studies on VTE prophylaxis suggests that active, multifaceted strategies.
Monthly Archives: April 2019
PAI-1 in the liver as an important candidate for alcohol mediated inflammatory damage
ApoRII expression correlates with serum adiponectin, steatosis, and liver fibrosis. Increased adiponectin levels, without an actual protective effect might even indicate a crosstalk from liver to adipose tissue, initiating a compensatory mechanism. Further studies are 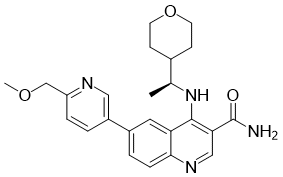 warranted to establish adiponectin as possible marker for monitoring of metabolic liver diseases. Furthermore, the current lack in mechanistical understanding of adiponectin signaling within the liver and the regulatory mechanisms in adipose tissue for adiponectin production should be targeted to evaluate this axis as drug target for ALD or NAFLD. A crucial result of the presented work is the ability of a small set of non-invasive parameters to discern NAFLD and ALD, as shown by the calculated machine learning methods. One major advantage of the presented algorithms is the wide availability of the used parameters. Self reported consumption of alcohol is not always reliable to establish either NAFLD or ALD. From a Gomisin-D clinical perspective it would be highly valuable to confirm or exclude ALD with high probability, without the need to rely on information given by the patient. Similarly RFs and DTs were able to discriminate between ALDC and ALDNC with very high accuracy. This was mainly due to inclusion of transient elastography, which can detect cirrhosis reliably when ascites or other disturbing factors are absent. Unfortunately this simple and highly informative method is not widely available, as a special ultra-sound head is needed to perform transient elastography measurements on tissue. Moreover, during patient recruitment cirrhosis was assessed by conventional ultra-sonography and transient elastography was performed as additional parameter. Though, to avoid confirmation bias from two sonographic methods, a second model to discriminate ALDC and ALDNC was calculated without transient elastography, which again yielded significant results. RFs and DTs offer the ability to assess importance of variables used for classification in a specific model. These importance Diacerein values can be used to find a minimal set of variables for the classification, thus reducing the amount of parameters which need to be determined and thus cost of a possible clinical application. Furthermore, assessment of importance enables more insights into the classification process and might even suggest underlying biological interactions, identifying interesting targets for disease monitoring or therapy. This is a clear advantage of DTs and RFs compared to other machine learning techniques that are rather black boxes, such as SVMs. It is noteworthy that in this model serum parameters of cell death and cytokines were the most important parameters for decision making. A previous approach for non-invasive fibrosis assessment in NAFLD yielded similar results. While the classic liver serum parameters are still important, as seen for discerning NAFLD and ALD, additional parameters as cell death markers, cytokines and adipokines should be collected routinely to monitor disease progression or for diagnostic purposes. Broad usage of those parameters may confirm current data in larger proportions of the general population. Limitations of the current study are the unavailability of liver tissue biopsies from the majority of patients. This unfortunately not only restricts exact pathological assessmentbut also excludes studies on cellular or molecular processes.
warranted to establish adiponectin as possible marker for monitoring of metabolic liver diseases. Furthermore, the current lack in mechanistical understanding of adiponectin signaling within the liver and the regulatory mechanisms in adipose tissue for adiponectin production should be targeted to evaluate this axis as drug target for ALD or NAFLD. A crucial result of the presented work is the ability of a small set of non-invasive parameters to discern NAFLD and ALD, as shown by the calculated machine learning methods. One major advantage of the presented algorithms is the wide availability of the used parameters. Self reported consumption of alcohol is not always reliable to establish either NAFLD or ALD. From a Gomisin-D clinical perspective it would be highly valuable to confirm or exclude ALD with high probability, without the need to rely on information given by the patient. Similarly RFs and DTs were able to discriminate between ALDC and ALDNC with very high accuracy. This was mainly due to inclusion of transient elastography, which can detect cirrhosis reliably when ascites or other disturbing factors are absent. Unfortunately this simple and highly informative method is not widely available, as a special ultra-sound head is needed to perform transient elastography measurements on tissue. Moreover, during patient recruitment cirrhosis was assessed by conventional ultra-sonography and transient elastography was performed as additional parameter. Though, to avoid confirmation bias from two sonographic methods, a second model to discriminate ALDC and ALDNC was calculated without transient elastography, which again yielded significant results. RFs and DTs offer the ability to assess importance of variables used for classification in a specific model. These importance Diacerein values can be used to find a minimal set of variables for the classification, thus reducing the amount of parameters which need to be determined and thus cost of a possible clinical application. Furthermore, assessment of importance enables more insights into the classification process and might even suggest underlying biological interactions, identifying interesting targets for disease monitoring or therapy. This is a clear advantage of DTs and RFs compared to other machine learning techniques that are rather black boxes, such as SVMs. It is noteworthy that in this model serum parameters of cell death and cytokines were the most important parameters for decision making. A previous approach for non-invasive fibrosis assessment in NAFLD yielded similar results. While the classic liver serum parameters are still important, as seen for discerning NAFLD and ALD, additional parameters as cell death markers, cytokines and adipokines should be collected routinely to monitor disease progression or for diagnostic purposes. Broad usage of those parameters may confirm current data in larger proportions of the general population. Limitations of the current study are the unavailability of liver tissue biopsies from the majority of patients. This unfortunately not only restricts exact pathological assessmentbut also excludes studies on cellular or molecular processes.
Under normal physiological conditions a balance is maintained between oxidative and antioxidant systems
By Horrigan and Aldrich to describe gating of the large conductance calcium-activated K + channels. This model is attractive because it explicitly partially decouples the activation status of components of the gating ring from the opening of the pore. The gating properties of the four different HCN isoforms and heteromeric assemblies thereof show marked differences with respect to cAMP regulation of gating. Thus, HCN2 and 4 form channels whose slowand very slowactivation is strongly enhanced by cAMP, HCN1 forms channels whose activation is relatively fastbut only modestly promoted by cAMPwhile HCN3 channels have basal kinetics similar to HCN2but they have the unusual property of being either insensitive to, or inhibited by, cAMP. It will be interesting to determine whether Mg2+ block of each subunit, especially HCN3, tracks the cAMPsensitivity of gating of the various isoforms or displays a distinct behavior. Given that the auxiliary protein, TRIP8b associates with the C-terminus of HCN channels and Pancuronium dibromide alters cAMP responsiveness, the nature of cAMP-regulated Mg2+ block in the presence of this protein is of particular interest. Scientific landscape shows a great attention for emotional intelligence. However, the definition of this construct remains somewhat elusive, with a number of competing models emerging in the literature in recent decades. Bar-On’s model is one of the most prevalent models in the literature, comprising a global trait EI dimension, five broad factors, and 15 more narrow facets. It broadly conceptualizes EI as “an array of non-cognitive capabilities, competencies, and skills that influence one’s ability to succeed in coping with environmental demands and pressures”. However, the measure based on this model, the Emotional Quotient Inventory, is most appropriately viewed as a measure of trait EI, since it Estradiol Benzoate assesses typical rather than maximum performance. Trait EI is an umbrella construct that integrates the range of personality traits linked to emotions; it represents the affective dimension of personality. Regardless of whether the focus is on the trait or ability dimension, a challenge with EI is to determine the set of measurable manifestations, which explains the large quantity of models that have emerged over the years. A critique levelled against Bar-On’s model is that it is over-inclusive, comprising a large quantity of social and emotional skills that determine how we understand ourselves and others, how we relate to others, and how we cope with  daily activities. In particular, it has been suggested that some of these factors are too broad and conceptually unrelated to EI. In order to improve our understanding of this construct, researchers have emphasized the necessity to explore its biological basis. To date, however, the role of biological factors has not been examined across the EI literature. The present study provides a starting point for research in this promising area, seeking to identify biological factors implicated in typical-performance or trait EI. Biological factors potentially related to EI are the molecules involved in the regulation of oxidative and antioxidant processes, which were found to play an important role in neuropsychological diseases characterized by cognitive impairment, in elicitation of mood types, such as anxiety in healthy women, and in depression among clinical patients.
daily activities. In particular, it has been suggested that some of these factors are too broad and conceptually unrelated to EI. In order to improve our understanding of this construct, researchers have emphasized the necessity to explore its biological basis. To date, however, the role of biological factors has not been examined across the EI literature. The present study provides a starting point for research in this promising area, seeking to identify biological factors implicated in typical-performance or trait EI. Biological factors potentially related to EI are the molecules involved in the regulation of oxidative and antioxidant processes, which were found to play an important role in neuropsychological diseases characterized by cognitive impairment, in elicitation of mood types, such as anxiety in healthy women, and in depression among clinical patients.
The effects of drugs with pleiotropic effects on the immune system or the aortic wall such as statins
Angiotensin converting enzyme and angiotensin receptor inhibitors could not be evaluated. In conclusion, aPLs occurring in AAA patients are associated with increased serological markers of inflammation and predicted progressive disease. These findings further Sipeimine support the concept of possibly underlying immune-mechanisms in AAA development. No association was observed between aPLs and the presence or size of an intra-aneurysmal thrombus. There is increasing interest in the role of nucleotides in immune and inflammatory responses, and in particular their role in lung diseases. There are currently known to be eight subtypes of G protein coupled P2Y receptorsand seven subtypes of ionotropic P2X receptorswhich respond to purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, and nearly all of these subtypes can be found on cells in the airways. It has been suggested that ATP may play a role in the pathogenesis of asthma, and allergen challenge has been shown to result in an increase in ATP in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from asthmatic patients. In a mouse model of asthma, allergen challenge also 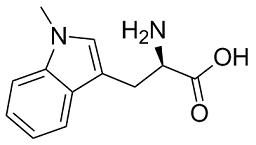 resulted in an increase in ATP concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluidand caused asthma-like symptoms which could be inhibited by administration of apyraseor by non-selective ATP antagonists such as suramin. These findings were interpreted as indicating recruitment and activation of lung dendritic cells by ATP, resulting in induction of asthmalike responses. The P2X7 receptor has been suggested to be involved in this process, and P2X7 knockout mice display reduced airway reactivity and leukocyte recruitment. The P2X7 receptor is known to play a key role in the processing and release of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1b, and in patients with asthma P2X7 receptors are upregulated on eosinophils and on macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, which secreted larger amounts of IL-1b in response to a P2X7 agonist. Reduced P2X7 function was associated with a lower incidence of asthma in children at high risk of the disease. Emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseare smoking-related lung diseases in which ATP has been suggested to play a role. In studies in mice, exposure to cigarette smoke increased the amount of ATP in BALF, and this was associated with inflammation and emphysema. Cigarette smoke caused the release of ATP from neutrophils, an increase in ATP in BALF and upregulation of P2 receptors on neutrophils, macrophages and lung tissue. Both cigarette smoke and ATP caused the release of the chemokine CXCL8 and elastasewhich could be prevented by suramin or apyrase. Suramin also reduced the smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema, and genetic deletion of the P2Y2 receptor reduced the smokeinduced production of cytokines including IFN-c and IL-1b and was also protective against smoke-induced inflammation. In a human study comparing non-smokers, healthy smokers and patients with COPD, there was a progressive increase in these groups in ATP levels in BALF, acute smoke exposure led to a further increase in the smokers and ATP levels were negatively correlated with lung function in the COPD patients. Tubeimoside-I Exhaled breath condensates from patients with COPD contained higher levels of purines than those from healthy subjects, and the levels correlated with the severity of the disease. In addition, enhanced responses to ATP were found in blood neutrophils and airway macrophages taken from patients with COPD, and there was upregulation of P2Y2 and P2X7.
resulted in an increase in ATP concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluidand caused asthma-like symptoms which could be inhibited by administration of apyraseor by non-selective ATP antagonists such as suramin. These findings were interpreted as indicating recruitment and activation of lung dendritic cells by ATP, resulting in induction of asthmalike responses. The P2X7 receptor has been suggested to be involved in this process, and P2X7 knockout mice display reduced airway reactivity and leukocyte recruitment. The P2X7 receptor is known to play a key role in the processing and release of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1b, and in patients with asthma P2X7 receptors are upregulated on eosinophils and on macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, which secreted larger amounts of IL-1b in response to a P2X7 agonist. Reduced P2X7 function was associated with a lower incidence of asthma in children at high risk of the disease. Emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseare smoking-related lung diseases in which ATP has been suggested to play a role. In studies in mice, exposure to cigarette smoke increased the amount of ATP in BALF, and this was associated with inflammation and emphysema. Cigarette smoke caused the release of ATP from neutrophils, an increase in ATP in BALF and upregulation of P2 receptors on neutrophils, macrophages and lung tissue. Both cigarette smoke and ATP caused the release of the chemokine CXCL8 and elastasewhich could be prevented by suramin or apyrase. Suramin also reduced the smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema, and genetic deletion of the P2Y2 receptor reduced the smokeinduced production of cytokines including IFN-c and IL-1b and was also protective against smoke-induced inflammation. In a human study comparing non-smokers, healthy smokers and patients with COPD, there was a progressive increase in these groups in ATP levels in BALF, acute smoke exposure led to a further increase in the smokers and ATP levels were negatively correlated with lung function in the COPD patients. Tubeimoside-I Exhaled breath condensates from patients with COPD contained higher levels of purines than those from healthy subjects, and the levels correlated with the severity of the disease. In addition, enhanced responses to ATP were found in blood neutrophils and airway macrophages taken from patients with COPD, and there was upregulation of P2Y2 and P2X7.
Obtained using spectral patterns from a homogenous population of cell suspensions
Recently, non-homogenous tissue based methods have been developed for proteomic and lipidomic analysis, and they appear to be reliable for tumor classification for digestive, brain, lymphomatous, and lung cancers. Among these tissue-based methods, MALDI-Tubuloside-A imaging is now used by several teams for clinical research. However, the MALDI-imaging approach remains complex because it requires frozen tissue slice analysis results to co-register MALDI spectra imaging and morphology imaging. For human liver metastasis samples, this method allowed tumor classification into six common cancer types with a sensitivity varying from 54% to 88%, and a specificity varying from 90% to 98% depending on the malignant class. To simplify the process, Lee and coauthors proposed performing MALDI-ToF MS for lipidomics analysis of preselected frozen section slices containing at least 70% malignant cells. The resulting spectra were used to generate a modelthat accurately classified normal lung tissues, lung tumor tissues, and primary NSCLC. Primary NSCLC was accurately discriminated from other types of lung tumors, and the three subclasses, adenocarcinoma, squamous-cell and large-cell carcinoma, were correctly discriminated and classified with a sensitivity and a specificity of 84% and 77%, respectively for adenocarcinoma versus squamous cell carcinoma. The authors recorded no misclassified sample when comparing Primary NSCLC and other types of lung tumors, whereas in the present study, we found both false negatives and false positives when we compared Primary lung cancer versus Metastasis subclasses. The difference in our study sample size, with greater numbers of tumoral and non-tumoral samplescompared to the above-mentioned study, could explain differences in diagnostic performance results. In addition, good diagnostic performance from other studies was achieved by applying MALDI-imaging on chosen regions that contained high tumor cellularitybased on the histology of sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Here, we used no pre-selection of tissue samples and obtained good results. We targeted tumoral pieces larger than 1 cm which represent the most frequent surgical indications. It is plausible that the size of the tumor have favorably influenced our results since the risk of having sampled a bad territory is reduced with large Epimedoside-A tumors as compared to millimeter tumors. Mass spectrometry imaging strategies offer the  advantage of conserving tissue but require sufficient surface area of tissue sections to obtain valuable information. In addition, MS imaging methods require trained experts, heavy analysis software and highthroughput signal acquisition instrumentation. Like these abovementioned methods, our strategy did not require any purification or standardization of the tissue cell content. Our crushed sample MS analysis was rapid, reproducible and very easy to perform. The non-conservative aspect of our approach was in part counterbalanced by the very low tissue sample sizeable to give valid spectra. Finally, using a simplified and non-image-guided method and larger cohort of patients, we obtained diagnostic performances similar to those obtained with MALDI-imaging methods or purified cell line methods. This surprising result could be due to more the complete information contained in complete unpurified tissue sample and to our modest objective, which was not to identify the exact nature of the tumor but to classify the sample into either the Cancer or non-tumor class.
advantage of conserving tissue but require sufficient surface area of tissue sections to obtain valuable information. In addition, MS imaging methods require trained experts, heavy analysis software and highthroughput signal acquisition instrumentation. Like these abovementioned methods, our strategy did not require any purification or standardization of the tissue cell content. Our crushed sample MS analysis was rapid, reproducible and very easy to perform. The non-conservative aspect of our approach was in part counterbalanced by the very low tissue sample sizeable to give valid spectra. Finally, using a simplified and non-image-guided method and larger cohort of patients, we obtained diagnostic performances similar to those obtained with MALDI-imaging methods or purified cell line methods. This surprising result could be due to more the complete information contained in complete unpurified tissue sample and to our modest objective, which was not to identify the exact nature of the tumor but to classify the sample into either the Cancer or non-tumor class.