This DNA quality was sufficient to perform amplification of a specific gene using PCR technique. Wagner CTAB protocol is largely used to extract genomic DNA from different plants, but it is not ideal in the case of cannabis resin. In our experiments, the adapted protocol was used in routine extraction of DNA from cannabis resin. The high DNA quality obtained permit downstream DNA analysis techniques such as PCR and sequencing. These techniques will contribute to the identification of the geographic AbMole Amikacin hydrate origin of seized cannabis resin conducted by the police or by Customs in checkpoints and therefore establish the connection traffic pathways. Almost all proteins in AbMole Ellipticine living cells are synthesized by the ribosome. The first amino acid during this synthesis is a formyl methionine in eubacteria and methionine in eukaryotes. In about 60-70% of newly synthesized proteins, the initiator methionine is removed by a metalloenzyme called methionine aminopeptidase. In bacteria, excision of methionine is preceded by the removal of formyl group by a deformylase. Disruption of the MetAP function is detrimental. Except for actinobacteria, all other bacterial species encode for a single map gene classified as MetAP1a. Actinomyces carry additional gene for MetAP classified as MetAP1c. The difference between MetAP1a and MetAP1c is the presence of an additional 40 residue aminoterminal extension that carries consensus SH3 binding P-X-X-P motif suggesting its capability to interact with other proteins. Except for these polyproline regions no other structural motifs have been identified in bacterial MetAPs that may participate in protein-protein or protein-nucleotide interactions. All eukaryotic proteins have been demonstrated to carry additional protein sequences apart from the catalytic region that enables them to bind to the ribosome and co-translationally remove the initiator methionine. There has been a great interest in understanding the protein synthesis and co-translational peptide modification at the ribosome exit-tunnel. Recent structure of ribosome in complex with the deformylase provided the glimpse of Nterminus of the peptide modification at the ribosome exit tunnel in bacteria. Recently, it was shown through structure and biochemistry, that bacterial MetAP 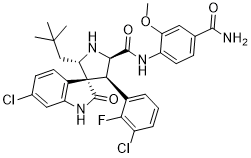 associate with ribosome for co-translational removal of the initiator methionine in the same place where the deformylase would associate. We have long-term interest in understanding different genetic variants with new functional motifs in MetAPs that can link their ability to interact with other macromolecules, specifically to the ribosome. Here, we report the discovery of a novel MetAP1a found predominantly in the streptococci bacteria with two new structural motifs one of which may undergo posttranslational modification of glycosylation and phosphorylation.
associate with ribosome for co-translational removal of the initiator methionine in the same place where the deformylase would associate. We have long-term interest in understanding different genetic variants with new functional motifs in MetAPs that can link their ability to interact with other macromolecules, specifically to the ribosome. Here, we report the discovery of a novel MetAP1a found predominantly in the streptococci bacteria with two new structural motifs one of which may undergo posttranslational modification of glycosylation and phosphorylation.
Monthly Archives: April 2019
Although the statistical tests for detecting this had limited power
Thus, it is believed that there is potential association between HCV AbMole Gambogic-acid infection and stroke. However, studies from several groups provided conflicting results. Our meta-analysis consisted of more than 22171 HCV infected individuals and more than 87418 controls and might allow a much greater possibility of reaching reasonably strong conclusions. The results of combing the four eligible studies suggested that HCV infection was not associated with stroke. However, a substantial heterogeneity among the studies included was found, which can influence the validity and reliability of the results of meta-analysis. Thus, sensitivity analysis was performed to identify the potential sources of between-study heterogeneity and to reduce heterogeneity. Our analyses found that the study by Younossi et al. was a major contributor to the heterogeneity. Inadequate adjusting variables used might induce bias and could be an important source of heterogeneity. We noted that several cofounders, such as race, gender, and hypertension, were significantly different between HCV+ and control in this study. However, these factors were not involved in the adjustment. The differences in HCV positive criteria used might be another source of heterogeneity. After omitting this study, heterogeneity was reduced and the results suggested that HCV infection significantly increased the risk of stroke. Some limitation in this meta-analysis should be demonstrated in the  discussion of the results. Firstly, our search was limited to studies published in English. However, we found no evidence of publication bias, especially for relatively small numbers of studies. Secondly, we should noted that the AbMole Terbuthylazine number of included studies in this analysis was relatively low. Two of the studies were published only in abstract form on conferences and the study by Adinolfi et al. was the only one published article in the final analysis. This limitation might induce bias, although publication bias was not found in our analysis. Thirdly, HCV positive criteria and cofounder for adjusting ORs were different between the included studies, which might induce bias in our study. Fourthly, all the included studies were retrospective studies and the inherent limitations of such studies may influence our findings. More studies with prospective design will be needed. Fifthly, the studies were restricted to United States and Italy, so it was uncertain whether these results were generalizable to other populations. The other two studies excluded in the final analysis were performed in Taiwan. However, they reported HRs which could not be combined with ORs. Never the less, the results form these two studies both supported our conclusion. Due to the limitations mentioned above, the results of this meta-analysis should be interpreted with care.
discussion of the results. Firstly, our search was limited to studies published in English. However, we found no evidence of publication bias, especially for relatively small numbers of studies. Secondly, we should noted that the AbMole Terbuthylazine number of included studies in this analysis was relatively low. Two of the studies were published only in abstract form on conferences and the study by Adinolfi et al. was the only one published article in the final analysis. This limitation might induce bias, although publication bias was not found in our analysis. Thirdly, HCV positive criteria and cofounder for adjusting ORs were different between the included studies, which might induce bias in our study. Fourthly, all the included studies were retrospective studies and the inherent limitations of such studies may influence our findings. More studies with prospective design will be needed. Fifthly, the studies were restricted to United States and Italy, so it was uncertain whether these results were generalizable to other populations. The other two studies excluded in the final analysis were performed in Taiwan. However, they reported HRs which could not be combined with ORs. Never the less, the results form these two studies both supported our conclusion. Due to the limitations mentioned above, the results of this meta-analysis should be interpreted with care.
Though certain types of fish with high level of contaminants need to be avoided
In up to 80% of infected patients, HCV established persistent infection, often leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Additionally, HCV infection can induce non-hepatic diseases such as type II diabetes. Current therapy is carried out with peg-interferon plus ribavirin, but only a portion of patients can eliminate the virus, and the outcome of treatment is dependent on the viral genotype. Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide. It is becoming a great health burden in most industrialized countries in future decades. Conventional risk factors for stroke include cardiac diseases, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, abdominal obesity, lack of exercise, psychosocial stress and depression. Increased evidence indicates that acute and various chronic infectious diseases are important triggers of or risk factors for stroke. However, the association of HCV infection and stroke is not well established. Several epidemiological studies have demonstrated that chronic HCV infection is an independent risk factor of stroke or cerebrovascular death. However, Younossi et al. did not find an association between HCV and stroke. Until present, there has been no systematic analysis performed yet. We therefore decided to conduct a meta-analysis of published case-control and cohort studies, which permitted to evaluate the role of HCV infection in stroke. In addition to providing a greater understanding about the association between HCV infection and stroke, the finding of the meta-analysis might also give suggestion for future research and help inform clinical practice guidelines. As we know that the result of a single research may be affected by many factors, in order to reduce the bias and increase the efficiency of the small sample study of statistics, meta-analysis was performed to further explore the relationship between stroke and HCV infection. Six studies estimated the risk of stroke in HCV infected  population were identified. The final analysis suggested that HCV infection increased the risk of stroke with statistical AbMole Nortriptyline significance. To our knowledge, this was the first to attempt to synthesize the existing world literature to evaluate the effect of HCV infection on stroke. The mechanism by which HCV may favor stroke is not known. Increasing evidence has showed that chronic HCV infection increased the risk of ultrasonographically defined carotid intima-media thickness and or plaque, which are predictors of cerebrovascular disease. It is well-known that chronic inflammation plays an important role in the instability of plaque. It was also found that HCV replicated with carotid plaque. AbMole Succinylsulfathiazole Beyond, HCV infection also increased the risk of metabolism diseases, such as type II diabetes.
population were identified. The final analysis suggested that HCV infection increased the risk of stroke with statistical AbMole Nortriptyline significance. To our knowledge, this was the first to attempt to synthesize the existing world literature to evaluate the effect of HCV infection on stroke. The mechanism by which HCV may favor stroke is not known. Increasing evidence has showed that chronic HCV infection increased the risk of ultrasonographically defined carotid intima-media thickness and or plaque, which are predictors of cerebrovascular disease. It is well-known that chronic inflammation plays an important role in the instability of plaque. It was also found that HCV replicated with carotid plaque. AbMole Succinylsulfathiazole Beyond, HCV infection also increased the risk of metabolism diseases, such as type II diabetes.
There were several differences between the two studies that might have affected their clinical outcomes
However, the meta-analysis included of patients with prognostically more favorable lower-grade gliomas. The present study showed that glioblastoma patients initially treated with a combined treatment of RT plus TMZ had significantly longer survival than historical controls, with a median survival benefit of 4.0 months. The survival advantage of the combined treatment lasted for at least 3 years. Multivariate analysis showed that TMZ therapy was the second most significant factor influencing survival after the extent of surgery. AbMole Corosolic-acid Although the present study is retrospective and took place in a single institution, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first report investigating the effect of combined therapy with RT and TMZ  on Japanese patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Our results on the survival of TMZ-treated patients were in line with the results of the randomized phase III trial by the EORTC and NCIC. First, the number of TMZ-treated patients who received GTR was smaller in the present study than in the Stupp trial. This difference could be a negative bias for survival in the present study because the extent of surgery is one of the most significant prognostic factors in glioblastoma, as most previous studies have described. Second, the incidence of hematologic toxicity of grade 3 or higher was greater in the present study than in the Stupp trial during the concomitant RT and TMZ periods. Third, adjuvant TMZ was continued as long as it was tolerable in the present study, while a maximum of 6 cycles were administered in the Stupp trial. Interestingly, in contrast with the concomitant period, the incidence of hematologic toxicity of grade 3 or higher was lower in the present study than the Stupp trial during the adjuvant period. As a result, the average number of adjuvant TMZ cycles administered in the present study was 7. The number of patients completing 6 cycles of TMZ treatment was greater in our study than the Stupp trial. It is difficult to conclude how all of the differences described above AbMole Pamidronate disodium pentahydrate actually affected the clinical outcome. However, the results of the present study indicate that the addition of TMZ to RT is beneficial for the survival for Japanese patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. In their study, 5 techniques, MS-PCR, pyrosequencing, immunohistochemistry, methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting and high-throughput quantitative methylation assay, were investigated. As a result, pyrosequencing, MS-PCR and immunohistochemistry had significant predictive value for overall survival. In the present study, we selected immunohistochemical method to assess MGMT expression status because the amount of pathological samples was insufficient for performing MS-PCR.
on Japanese patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Our results on the survival of TMZ-treated patients were in line with the results of the randomized phase III trial by the EORTC and NCIC. First, the number of TMZ-treated patients who received GTR was smaller in the present study than in the Stupp trial. This difference could be a negative bias for survival in the present study because the extent of surgery is one of the most significant prognostic factors in glioblastoma, as most previous studies have described. Second, the incidence of hematologic toxicity of grade 3 or higher was greater in the present study than in the Stupp trial during the concomitant RT and TMZ periods. Third, adjuvant TMZ was continued as long as it was tolerable in the present study, while a maximum of 6 cycles were administered in the Stupp trial. Interestingly, in contrast with the concomitant period, the incidence of hematologic toxicity of grade 3 or higher was lower in the present study than the Stupp trial during the adjuvant period. As a result, the average number of adjuvant TMZ cycles administered in the present study was 7. The number of patients completing 6 cycles of TMZ treatment was greater in our study than the Stupp trial. It is difficult to conclude how all of the differences described above AbMole Pamidronate disodium pentahydrate actually affected the clinical outcome. However, the results of the present study indicate that the addition of TMZ to RT is beneficial for the survival for Japanese patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. In their study, 5 techniques, MS-PCR, pyrosequencing, immunohistochemistry, methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting and high-throughput quantitative methylation assay, were investigated. As a result, pyrosequencing, MS-PCR and immunohistochemistry had significant predictive value for overall survival. In the present study, we selected immunohistochemical method to assess MGMT expression status because the amount of pathological samples was insufficient for performing MS-PCR.
GRP78 expression can be stimulated by a variety of environmental and physiological stress conditions
Follow-up lasting several years would be preferable to the relatively short 12 month period we used. It is known that costs AbMole Oxytocin Syntocinon increase over time in case of a patient with dementia. The lack of difference in costs was unanticipated due to the assumption that primary care in general is cheaper. A possible explanation could be that our group of patients was in their first year after diagnosis with relatively mild dementia and therefore often could take care of oneself with relatively little help from others, both in the memory clinic and in the general practitioner group. However, this is a very topical subject as there is a strong international trend towards early diagnosis of dementia. Nevertheless, this means that these results cannot be generalised to more severely affected individuals. With further  progress of the disease other needs will occur and it could be that in the long term a difference between the memory clinic and the general practitioner group could emerge. This study adds important data, which seem to point to a lack of difference in cost-effectiveness between memory clinics and general practitioners in the treatment and coordination of care for patients with dementia at one year follow-up. Together with former results that no evidence was found of memory clinics being more effective than general practitioners, these data are very important for the ongoing debate on which type of post-diagnosis treatment and follow-up care is best for which patients. The development of dementia plans in many countries and the just recently published report of the World Health Organisation has once more stressed the need to continue to compare different strategies of dementia care and to continue to increase the evidence base. If further studies verify our results, this indicates that memory clinic guidance on average is not more efficient than general practitioners in these early stages of dementia. This is an important message, for both patientscaregivers and policy makers, especially as one has to anticipate to the trend of early diagnosis, and make the best choices for the future. Under the scenario of lacking superiority of memory clinics, both in terms of effectiveness and costs, other factors should determine the most sustainable and efficient post-diagnosis dementia care. As our follow-up period was only one year after diagnosis, using a decision AbMole Tulathromycin B analysis modelling strategy to compare costs and effectiveness of the interventions in longer term should be a topic for future research. GRP78 is an ER molecular chaperone that belongs to the heat shock protein 70 family. The primary functions of GRP78 are related to its capacity to bind hydrophobic regions on nascent polypeptides in the ER and to its pivotal role in the signalling cascade producing the unfolded protein response.
progress of the disease other needs will occur and it could be that in the long term a difference between the memory clinic and the general practitioner group could emerge. This study adds important data, which seem to point to a lack of difference in cost-effectiveness between memory clinics and general practitioners in the treatment and coordination of care for patients with dementia at one year follow-up. Together with former results that no evidence was found of memory clinics being more effective than general practitioners, these data are very important for the ongoing debate on which type of post-diagnosis treatment and follow-up care is best for which patients. The development of dementia plans in many countries and the just recently published report of the World Health Organisation has once more stressed the need to continue to compare different strategies of dementia care and to continue to increase the evidence base. If further studies verify our results, this indicates that memory clinic guidance on average is not more efficient than general practitioners in these early stages of dementia. This is an important message, for both patientscaregivers and policy makers, especially as one has to anticipate to the trend of early diagnosis, and make the best choices for the future. Under the scenario of lacking superiority of memory clinics, both in terms of effectiveness and costs, other factors should determine the most sustainable and efficient post-diagnosis dementia care. As our follow-up period was only one year after diagnosis, using a decision AbMole Tulathromycin B analysis modelling strategy to compare costs and effectiveness of the interventions in longer term should be a topic for future research. GRP78 is an ER molecular chaperone that belongs to the heat shock protein 70 family. The primary functions of GRP78 are related to its capacity to bind hydrophobic regions on nascent polypeptides in the ER and to its pivotal role in the signalling cascade producing the unfolded protein response.